Piglets commonly suffer from a splaying out of the limbs soon after birth, which can severely compromise their ability to suck and to escape from under the sow.
The overall incidence of the condition is unknown but can occur:-
a) As a sporadic outbreak over a short period of time - affecting 20% or more of pigs.
b) As an occasional condition in isolated pigs or litters.
c) As a longstanding grumbling problem in a herd.
The condition in itself is not fatal - death being due to a combination of starvation, chilling and crushing - and as such the mortality is highly variable, depending on the level and quality of nursing offered to the piglets. Where husbandry and stockmanship is inadequate, mortality can approach 100% of affected piglets.
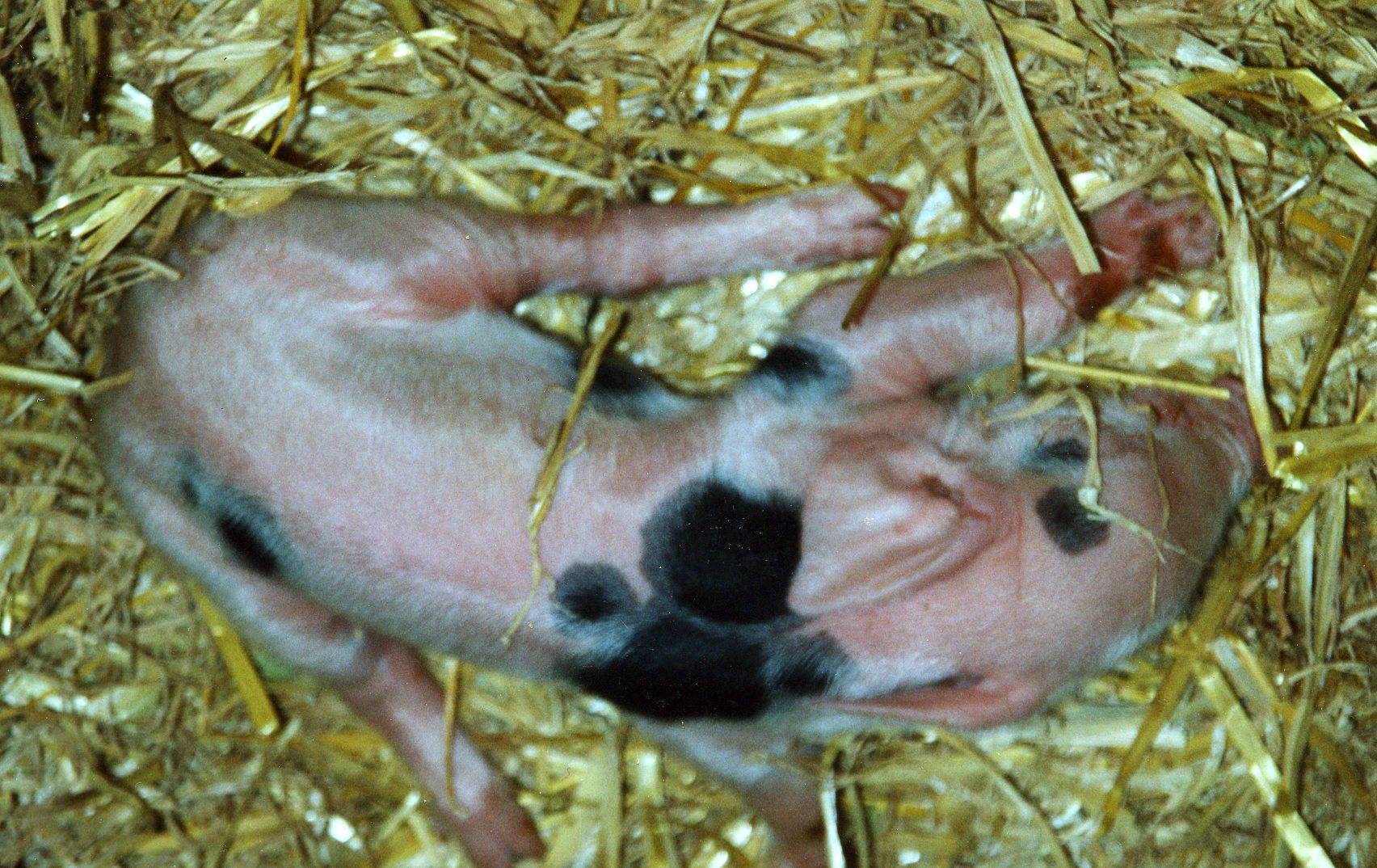
Fig 1: Four legged splay 'Star'

Fig 2: Hind Limb splay - the most common

Fig 3: Front legs only affected by splaying (PRRS form).
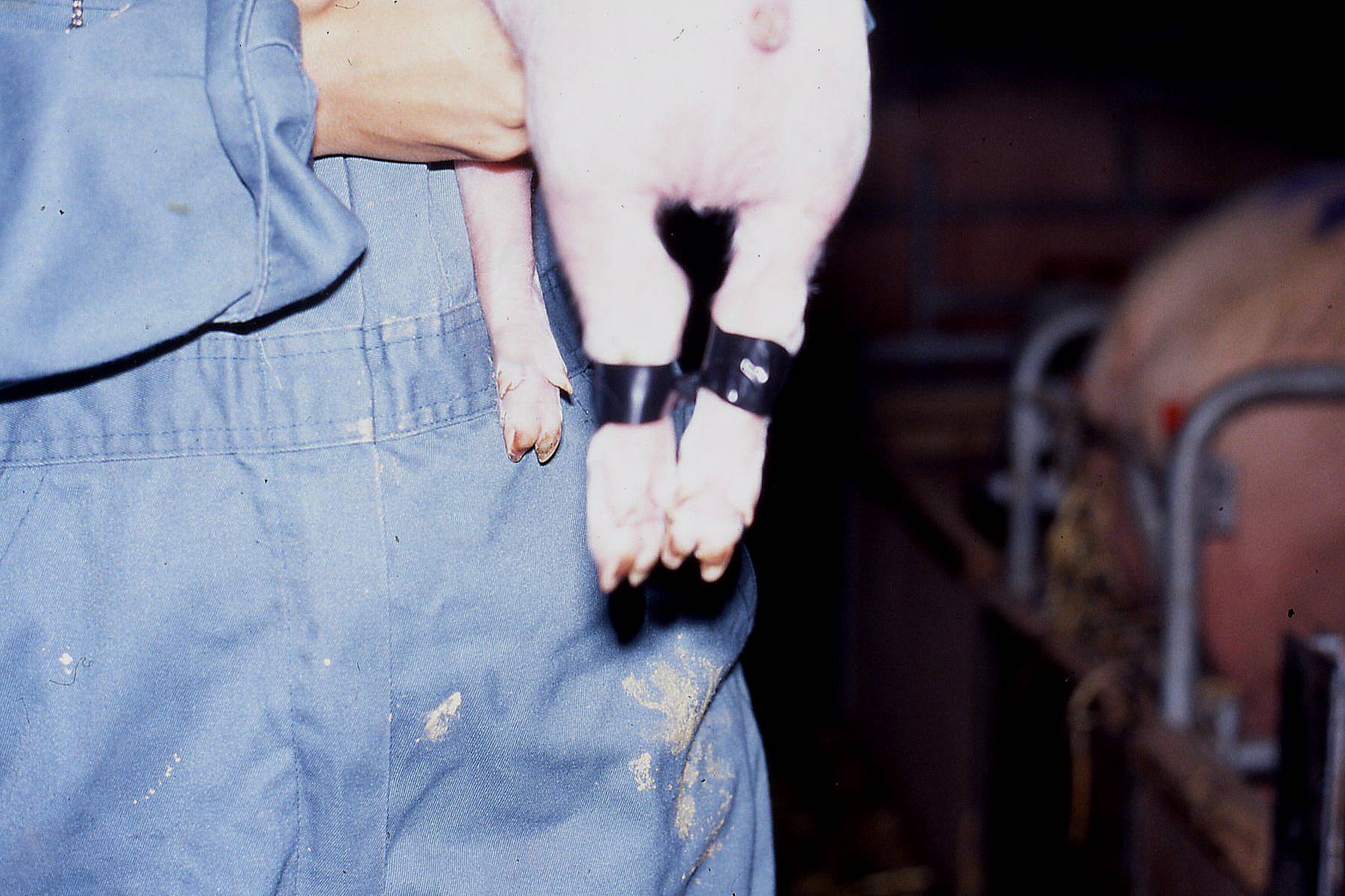
Fig 4: Taping of hocks
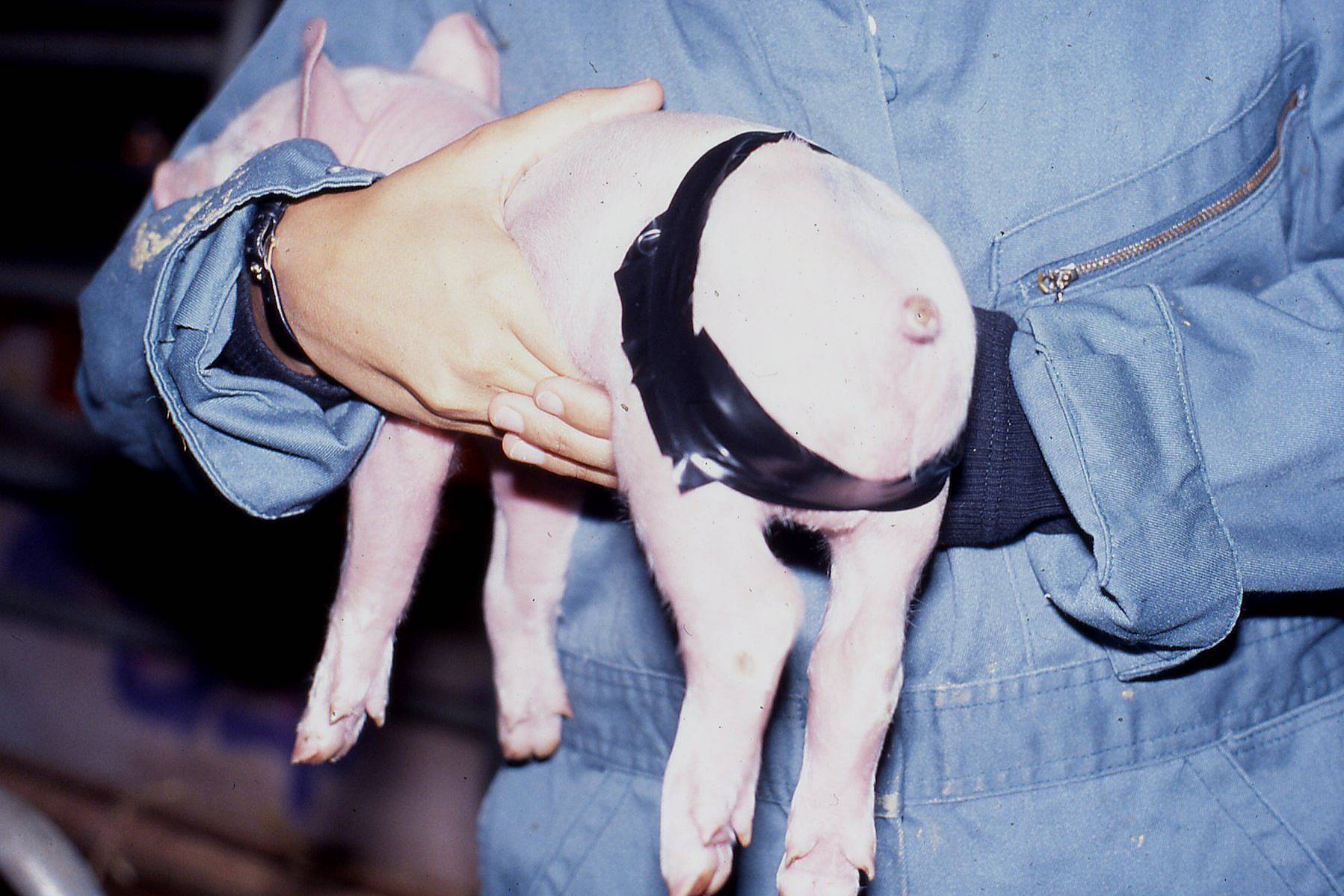
Fig 5: Taping of hips
Presentation
The condition is seen at or soon after birth and can present in a number of forms:-
1) "Stars". In these pigs, both sets of limbs are splayed out sideways, such that the pig cannot stand and can only get about by crawling or shuffling.
2) Hind Leg Splays. This is the most common form of the condition. The back legs splay out sideways and forward causing the pig great difficulty in standing on its hind end. Many will "dog sit" and shuffle around on their backsides. This can lead to considerable trauma to the skin of the perineum and vulva and secondary infection.
3) Front Leg Splays. This is extremely rare - only seen at the height of a PRRS outbreak in the early days of the disease. The hind limbs work normally but the front legs splay out sideways such that the pig moves around with its chin on the floor. Such pigs have great difficulty sucking and mortality levels are high.
Causes
Splayleg is a truly multifactorial condition, although the 2 least common presentations - front leg splay and "stars" - appear to be usually associated with the teratogenic effects of infection, disease or even toxicity in the dam during late pregnancy, which may affect either nerve or muscle development. Both conditions occur, for example, during acute outbreaks of PRRS and are typically short lived outbreaks.
Hind leg splays - the most common form - however, are less clear cut. In general, the condition is more common:-
1) In the Landrace breed type.
2) In smaller weaker piglets
3) In piglets born onto wet slippery floors (it is uncommon in the outdoor herds).
4) In association with Congenital Tremor type AII - which is believed to be caused by a novel pestivirus affecting naïve sows and gilts in early to mid pregnancy .
5) There is no proven seasonal influence
A possible explanation for the development of the condition is that certain piglets may be born with a weakness in their adductor muscles - those responsible for holding the back legs together - as a result of either genetic or developmental weakness - the latter resulting from nutritional, environmental, infectious or managemental insult to the sow, probably in the later stages of pregnancy. Mycotoxins affecting the pregnant sow have also been implicated.
The pig is then born into an environment where it struggles to keep its legs together, the muscles are strained and damaged making it difficult and/or painful to contract them and hold the legs together. This damage will occur as a result of the normal "scrabbling" for a teat in which the natural motion of the hindlegs is backwards and outwards. Better grip is provided by a bedded pen but some slatted floor types are less likely to be associated with splayleg than others eg plastic slats v metal bar slats.
Prevention
Where splayleg is recognised as a significant condition within a herd, it is necessary to review, with your veterinary surgeon, all the factors which may be contributing to the problem. This will include breeding policy, housing and husbandry of the pregnant sow, nutritional management and a review of flooring in the farrowing area. The provision of copious bedding around the farrowing period may help to reduce the incidence of the condition. Shredded paper may be useful on fully slatted floors. Alternatively, latticed rubber matting (sold as safety matting for swimming pools) can be used behind the sow during farrowing. This is particularly useful on high risk flooring materials such as metal bar slats eg Tribar.
Treatment
Survival of front leg splays and "stars" is very poor and, in general, early euthanasia may be the best option.
For hind leg splays, recovery can be excellent if time and care are provided. In the first few hours the piglet may require assistance to suck to ensure a reasonable intake of colostrum. Assisted sucking to ensure early and adequate colostrum intake alternating with boxing away, under a heat lamp for the first 24-48 hours, can reduce overlaying losses in compromised pigs. The traditional method of treating such pigs involves tying the back legs loosely together below the hocks. Insulating tape works reasonably but must be checked daily and removed before it cuts in to the skin. Specially made hobbles using Velcro are also available and are re-useable; string and baler twine are not acceptable due to injury they cause.
Considering that it is the upper muscle masses of the leg, which control the hip joints, which are compromised, better results may be achieved by taping the hips together. Again, insulating tape works well and should pass over the back in front of the pelvis, down either side to cover the leg below the hip joint to meet at the back below the tail underneath the anus/vulva. Again, do not leave the tape on too long (3-5 days should be plenty); do not make it too tight and do not block the anus/vulva. (Fig 5.)
The most labour intensive but more effective treatment is massage. Vigorous working of the muscles of the upper leg and rump using thumb and forefinger for 5 minutes every few hours in the first day or 2 of life can give an extremely good recovery rate. If undertaken, the legs should not be taped as the idea is to encourage muscle development and this will not occur if the muscles are not working.
Where splayleg occurs in conjunction with congenital tremor a high level of stockmanship input is necessary to avoid excessive losses. Assisted sucking or even artificial feeding may be necessary to keep pigs alive long enough for them to recover with attention to hind legged splaying as above a supplementary requirement. Severly affected pigs should be humanely euthanased.
Costs
No specific costings are available for splayleg on a national basis and the costs involved on an affected farm will depend on the extent of the problem.
Costs are incurred:
- As a result of additional labour needed to nurse affected pigs.
- Mortality associated with affected pigs. With a weaned pig worth in the order of £30 (at 2015 prices) a 1% mortality due to splayleg in a 600 sow breeding herd will cost nearly £5,000 per year.

